Knowing about the Colorado independent contractor guidelines can save you some headaches and tons of money! Entrepreneurs and workers alike should also distinguish an independent contractor from an employee as misclassifying the people you work with comes with huge penalties. Chances are you would pay double or even triple an individual’s salary if you mistakenly categorize one properly.
Independent Contractor vs Employee: What are the Differences?
The differences between an employee and an independent contractor can be tricky at times. The lack of legal information can sometimes blur the lines between the two, making the business owner vulnerable to error and lawsuits.
If you are a business owner who hires several people for your company, understanding the Colorado independent contractor guidelines would be a lifesaver.
What Makes an Employee?
Workers are considered employees if the company withholds their taxes, Medicare, and social security. The company also has full control over its work and how they do it.
What Is an Independent Contractor According to Colorado Independent Contractor Guidelines?
According to the Colorado independent contractor guidelines, independent contractors are free from a company’s control over their work performance and work hours. Independent contractors are also exempted from insurance and other benefits unless specified in their contract.
For employment tax purposes, the usual common law rules are applicable to determine if a worker is an independent contractor or an employee. Under common law, you must examine the relationship between the worker and the business. You should consider all evidence of the degree of control and independence in this relationship. The facts that provide this evidence fall into three categories – Behavioral Control, Financial Control, and Relationship of the Parties.
The Three-Factor Test- Updated from Fall 2022
To be safe, business owners use a three-factor test to determine whether an individual would be classified as an employee or an independent contractor.
The Behavioral Test
The behavioral test helps determine whether an individual is an employee or an independent contractor by the way the job gets done.
Behavioral Control covers facts that show if the business has a right to direct and control what work is accomplished and how the work is done, through instructions, training, or other means.
- Do you regularly report to a manager regarding your work?
- Is your performance regularly evaluated?
- Are you provided with occasional training related to your job?
- Are you free to work anytime and anywhere convenient for you?
- Are you tied to the company’s rules and regulations?
- Do you follow a fixed work schedule?
The Financial Test
The financial test provides a strong indication that an individual is either an employee or an independent contractor.
Financial Control covers facts that show if the business has a right to direct or control the financial and business aspects of the worker’s job. This includes:
- How are you paid and how regularly – monthly, weekly, or fortnightly?
- Are you eligible for reimbursements? Do you have unreimbursed business expenses?
- Do you use the company’s resources, or do you provide for your own?
- Do you pay for your own health insurance, liability insurance, and other insurance?
- What extent do you make your services available to the relevant market?
- What extent can you realize a profit or incur a loss?
The Relationship Test
The relationship test covers issues that establish your relationship with your client or employee through certain provisions.
Relationship of the Parties covers facts that show the type of relationship the parties had. This includes:
- Do you receive employee-type benefits like: fringe benefits, insurance, a pension plan, paid sick days, and vacation leave pays?
- Do you offer specific services or are you forced specific projects?
- Do you have a written contract or oral agreement with your client, which favors you as an independent contractor or describes your intended relationship with the client?
- Do you furnish an invoice for every completed job or project?
- How permanent is the relationship for this job with the client?
- Are the services that you perform a key aspect of the regular business of the company?
These tests will ultimately determine whether you are classified as an independent contractor or an employee. Just as you have to be mindful of these critical details, your client or employers should, too, or they may face huge penalties.
Colorado Independent Contractor Taxes
Tax is a complex issue for regular employees, and even more for independent contractors. Colorado independent contractor taxes can be tedious considering that independent contractors are obligated to accomplish this on their own.
Basically, an independent contractor or self-employed individual pays several taxes – federal, state, income tax, and SECA (Self-Employed Contributions Act).
Do Independent Contractors Pay More Taxes Than Employees Do?
Regular employees and independent contractors have their respective tax obligations. Employees use the W-2 form while self-employed and independent contractors use the W-9 and 1099-NEC forms. Aside from this, the difference is that employees have less worry about submitting forms because their employers do this for them. On the other hand, independent contractors handle both the legwork and paperwork, not to mention the tax rates they pay can be higher depending on their earnings.
SECA Taxes
Employees are obligated to pay the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) tax, which is deducted from their salary. The amount collected depends on your gross pay. They pay half of the total cost while the other half is shouldered by the employer. This is a mandatory tax that goes to the social security and Medicare funds.
Independent contractors and self-employed individuals are required to pay FICA’s equivalent, the Self-Employed Contributions Act. Compared to FICA, self-employed individuals must pay 100% of their total cost, which also depends on their income. However, they can choose to declare half of it as a business expense. If the net income is $400, no SECA payment will be required. The standard SECA rate is 12.4%.
1099-NEC (Non-Employee Compensation)
The 1099-NEC form is used to report the total earnings from all business transactions made within the year. The form should be submitted to the IRS.
Form W-9
To report the income, contribution to an IRA, mortgage interest, real estate transactions, etc., an independent contractor must accomplish a form W-9, in which the Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) must be provided.
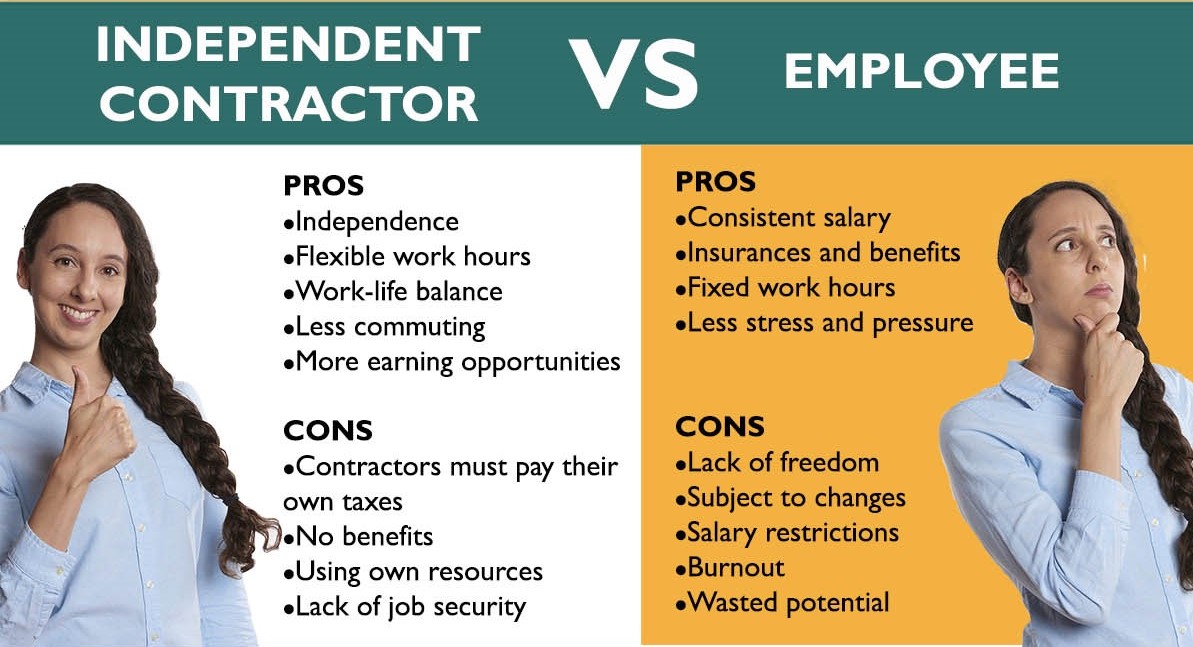
- There isn’t a right or wrong answer to whether you should hire an independent contractor or an employee. However, there may be a better option based on what they will be doing in your business and the independent contractor guidelines in Colorado. Learn about the pros and cons of being an independent contractor and an employee for Colorado small businesses.
Independent Contractor vs Employee—Pros and Cons
Working as an independent contractor have perks but there are also downsides. The same thing goes if you choose to be an employee. The pros for both may outweigh the cons and vice versa. The independent contractor vs employee pros and cons should help you decide which way to go.
Working as an Independent Contractor
There are several benefits of being an independent contractor that appeals to new graduates and seasoned professionals. But there are also disadvantages. Here are a few:
Pros
Independence
Working as an independent contractor offers you independence in many aspects. To a degree, you are your own boss. No manager will monitor the way you do work and dictate your limitations job-wise. To a lot of people, this is the highlight of being an independent contractor that is priceless.
The freedom from the usual eight-hour work shift is one of the best things about working independently. Without a 9-5 schedule, you are free to work at your most convenient time and not have to worry about tardiness, salary deductions, or poor rating.
Work-life balance
Being an independent contractor means less pressure. You are in control of your time and workload. When things get stressful, you can take the time off as you see fit. No need to ask for permission or wait for the approval. In an office setting, employees do not have the luxury of taking sick or vacation leaves unless allowed by a manager.
Less commuting
As an independent contractor, you cannot only choose when to work but also where to work. If the home is where your heart is, you can set up a home office and work from there. There is no need for a daily commute and dealing with traffic jams in the morning or evening.
You have the opportunity to earn more
The Colorado independent contractor guidelines do not restrict you from taking on as many projects as you can since you are not tied to a specific company. This gives you the freedom to work with multiple clients unless specified in the contract. You can also set your own price for the services your offer if your skill is in demand.
Cons
Colorado independent contractor taxes
According to the law in Colorado, independent contractor taxes must be paid by the contractor as they are also classified as self-employed. This means that if you are an independent contractor, you must withhold your own local, state, and federal taxes and submit your tax report to the IRS on your own. This can be a tedious process and missing deadlines could result in penalties.
No benefits
Being an independent contractor relieves you of employment and unemployment benefits. The responsibility of paying your own health insurance and other insurance falls on you. The rates of these insurances are usually higher for self-employed individuals. You may also have to fund your own retirement.
Covering your own resources
Aside from not paying taxes, insurance, and benefits, some employers like to hire independent contractors because they do not have to provide their own tools or resources. They are not even required to pay for out-of-pocket expenses. This means you will have to pay for utilities—internet, electricity, transportation, office supplies, etc.
Lack of job security
Being an independent contractor also comes with pressure. Competition can be tough especially now that contracting has become a favorable option for employers especially. Many people are offering their services as independent contractors like you do. To score clients, you sometimes have to be aggressive in promoting your skills, establishing your expertise, and maintaining a good track record. Other independent contractors are aware of this, too, so the competition is high, the reason you may find yourself jobless for a period of time until a new client signs you up.
Working as an Employee According to Colorado Independent Contractor Guidelines
So many good things have been heard about working as an independent contractor that becoming an employee almost becomes a poor choice. But remember that like an independent contractor setup, regular employment has its own merits and downsides.
Pros
Consistent monthly earnings
As an employee, you can let the company owners worry about project successes and failures and payment collections from clients. Keep doing your job and you are guaranteed to receive your monthly salary.
Insurances and benefits
Among the things that make an employee feel secure are paid sick days and vacation leaves, social security and tax payments, a retirement plan, health insurance, life insurance, and other employment/unemployment benefits paid out of your employer’s pocket.
Work ends when you clock out
As soon as the workday ends, you are free to spend the rest of the day with family and friends. Do whatever you want with the remaining time that you have and do not worry about work anymore if you choose to. As a regular employee, life and work are clearly separated instead of work becoming your life.
Less stress and pressure
Independent contractors can get caught up with their work as they sometimes must perform without limits especially when a project follows a strict deadline. This lifestyle can become stressful compared to a job with a fixed schedule.
Cons
Lack of freedom
You have the skills, and you know how to do a specific task. However, as an employee, you are obligated to follow what your manager or boss tells you. The work that you do is limited and often you have to rely on other people to complete a specific project. If your boss turns out to be a micro-manager, you can’t really complain.
Fixed work schedule
As an employee, you are tied to an eight or nine-hour work schedule. Your break times are scheduled and you are not free to leave the office for personal reasons if needed. Although you did sign up for this, the routine can still affect your efficiency. Sometimes, your schedule may also change depending on your manager’s instructions.
You are subject to changes
There are times when your job description may change at the employer’s discretion. You may also get transferred from one department to another as needed and you cannot complain about it especially if it’s stipulated in your contract. This is inconvenient and stressful especially if you have become comfortable with your team and environment.
Your salary may not be commensurate with your skills or qualifications
If you get hired for a position with a specific salary range, that is all you are going to get every payday after taxes. You can perform tasks not covered by your job description or take your work home and still get paid the same unless your boss offers you a bonus, which does not happen all the time.
Burnout
When you have a regular job, monotony can become an enemy. The routine can wear you out over time – wake up early, commute to the office, and go home. If you have been doing this for years, you may end up plateauing career-wise. When you get bored at work, you may lose interest in achieving more and be content with your status, as long as you get the job done and get paid for it.
Wasted potential
You could either get tired and lose interest in leveling up your career or be depressed because you fail to explore your potential. While it is good to keep a job for a long time, it tends to prevent you from growing and developing new skills. It would be too much to learn new things while buried in your own department. Instead of renewed zest for life, you might feel miserable in the process.
There are companies that would encourage their employees to develop their skills and provide the resources for this, but there are also those that are not capable to do this. But still, it happens.
Colorado Independent Contractor Guidelines: What Happens in Case of Misclassification?
Business owners should be extra careful in hiring independent contractors. It is critical to classify them properly and in accordance with the Colorado independent contractor guidelines. Be mindful of the three-factor test and make sure that all the necessary contracts are in place. Failing to do so may get you in trouble. The financial consequences are specified in Section 3509 of the Internal Revenue Code.
If the distinctions are confusing, you may want to seek help from a reliable business consultant who will help you with the manpower aspect of your business. It could save you a lot of time and money if you have knowledgeable people to back you when hiring workers for your company or project.
Steven J. Wick & Associates P.C. offers a variety of business-related services including business consulting to assist small, medium, and large business owners in worker classification. We also provide accounting and bookkeeping solutions to further empower your business and take it to the next level.
Steven J. Wick & Associates P.C. is here to help. Call us today!